Spend time in any modern office building in America and you’re likely to come across a standing desk. These work-altering pieces of furniture first gained traction in the workplace about twenty years ago, and have since gone on to become ubiquitous. The appeal, for adherents and companies alike, is the potential health benefit from standing versus sitting.
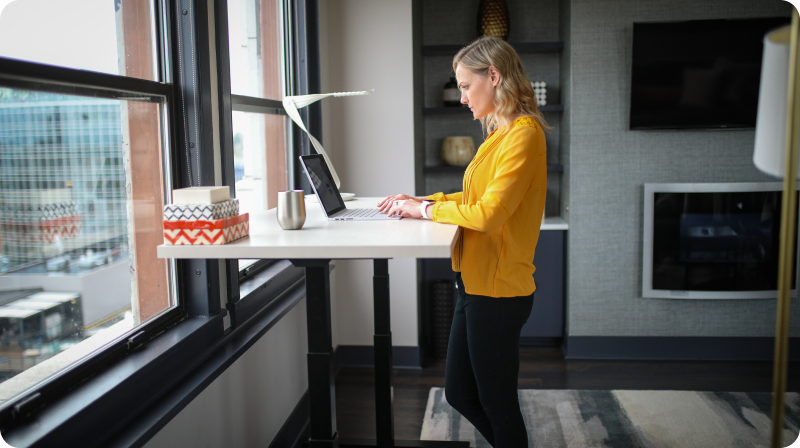

That benefit might not be as clear as originally thought. A study published in The Journal of Physical Activity and Health in 2016 calculated the calories spent standing at a desk, versus sitting. The study found that the increase was modest at best. This contradicts other studies that found standing burns significantly more calories—as much as 1,000 additional calories per week. The problem with the calculation in either case is that any given study can’t account for other variables. (For instance, people who choose to work at a standing desk may be more likely to walk during their lunch breaks—which would increase overall calorie burn even more significantly.)
The flip side is that standing incorrectly, or standing for long periods on a hard surface just because “you should” can lead to joint and muscle ailments and pain.
Want to give standing at work a shot? Follow these guidelines for integrating a standing desk:
-
Use an adjustable desk. Some “standing” desks are nothing more than fixed platforms that raise the level of your computer monitor. But people are different heights, meaning that one size never fits all when it comes to standing desks.
-
Stand correctly. Proper body positioning is exactly why you should buy an adjustable standing desk. Your forearms should rest at a 45 degree angle to your body, knees should be very slightly bent rather than locked out, and your natural eye level should be pointed right at the middle of the monitor.
-
Maintain posture. One the most common problems with standing desks is neck and back pain. It’s easy to get fatigued and slump forward. Check your posture every 15 minutes or so, to make sure your shoulders are erect and held right over your hips, and your chin is tucked.
-
Time out. It’s not a good idea to stand for the entire workday. That can lead to joint and muscle aches and other issues. Start out standing for 15 minutes and then sitting for the same amount of time. Increase your standing time day by day, until you can easily stand for 30 minutes at a time.
-
Keep comfortable. Any standing desk should be paired with a standing mat to limit fatigue, joint, and muscle pain. You should also wear comfortable shoes with superior arch support.
Show some love if you liked this post!