Traditional Chinese medicine offers a number of alternatives to pharmaceutical pain killers, primarily because those drugs weren’t available for much of the history of Eastern medical practices. One non-invasive treatment, called Gua Sha, involves dragging the smooth edge of an instrument across the skin, raising a rash-like pattern of red spots (known medically as petechiae).
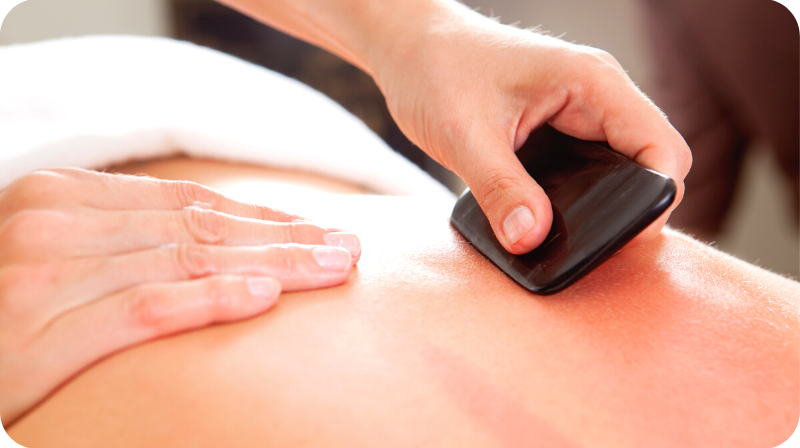

Gua Sha has traditionally been used to treat chronic pain anywhere in the body. Practitioners generally combine this practice with other alternative, holistic therapies such as acupuncture or acupressure.
The process itself is simple and painless. The practitioner coats the area of skin to be treated with a light layer of oil, and then uses a stone or specially prepared scraper made of bone to scrape the skin firmly, but not harshly.
A Multipurpose Alternative Treatment
Gua Sha does have a basis in fundamental science. Experts believe that the treatment significantly increases blood flow to the treated area, reducing toxins and prompting an immune response that speeds healing. That general theory of practice has led practitioners to use Gua Sha to treat a number of conditions, although it’s likely to be most effective for certain conditions.
- Migraines and cluster headaches. The results of a small inpatient study indicate that Gua Sha may be effective in reducing the severity of migraines.
- Muscle tics and spasms. Another preliminary study following a Tourette’s Syndrome patient found that symptoms were reduced by 70 percent, after the patient adopted a suite of changes in lifestyle, diet, holistic treatments, and Gua Sha. The results, although only a start, point to Gua Sha’s possible role in the treatment of back spasms that cause chronic pain, and as a tool in combatting pain and symptoms of diseases such as multiple sclerosis or ALS.
- Neck pain. A clinical trial revealed that Gua Sha was effective at relieving chronic neck pain. However, it appears the treatment would have to be repeated on an ongoing basis to maintain the pain reduction.
A modest amount of research supports using Gua Sha for a variety of conditions, and especially where chronic pain is a significant symptom. The good news is that there are few side effects other than a rash-like pattern on the skin that quickly resolves. The procedure itself is usually painless and some patients even find it relaxing and pleasant.